





Design Project 2Ba IWT, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, 2014

Stairclimbingrobot
Support surfaces
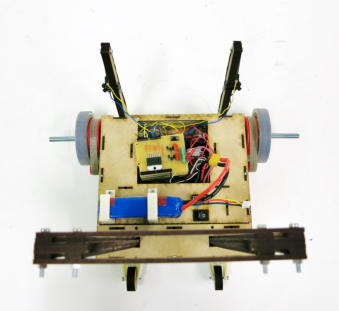
As with the wheels, different types of rubbers and silicones were used to achieve enough grip for the support surface, since the robot relies almost entirely on grip. At first a normal rubber with a ridged surface was used but was not effective enough. A counterweight was attached to the robot to increase the pressure on the support feet. A latter improvement was the use of mixing silicones. A rectangular mold was made and two pieces of Silicones were attached to the abs support which made the counterweight otiose.properties
In this section some of the major properties are mentioned in the form of a list. • Driving Speed: 0.43 km/h • Weight: 1,728 kg • Average time per stair: 14,47s • Dimensions: ̵ Height = 350 mm ̵ Length = 200 mm ̵ Width = 260 mm The robot uses two stepper motors to drive the wheels. One DC-motor is used to drive the racks. The case was made out of 3 mm thick MDF wood while the spurs were made out of Plexiglas or ABS. The support surfaces are also designed in ABS where a small layer of Silicones has been mounted on. A thicker layer of Silicones was used to cover the wheels and finally a sheet of aluminum has been fixed on the front of the conductors which minimizes friction and provides the robot a smooth motion as it is moving up- or down.Improvements
Spurs
The final gears used between the racks are made of Plexiglas or ABS with a module of 1.5. Originally the module was 1.0 but this made the robot fragile as broken spur teeth occurred. The size of the gears changed during the design process because the original system used two DC-motors so the spurs were not connecting. This system was originally chosen to keep the center of gravity on the midline of the robot. This advantage was sacrificed as a system with one DC-motor was favored.Racks
The toothed racks have a total length of 350 mm and a module of 1.5. The material used to build these is 3mm MDF. They consist of 6 pieces, each of which are not glued together. This gives a flexible advantage and reduces the risk of a rack breaking when they undergo some forces caused by the forward or backwards motion in the process of climbing a stair..Wheels
A series of different wheels were tried before we decided to create our own with a mold and pouring silicone. The first types where built with normal rubber, but were unable to provide enough grip for smooth driving. The new wheels are softer which helps the robot during the climbing of the stairs.